THE EFFECT OF CHEMICAL ACTIVATION AGENTS AND ACTIVATION TEMPERATURE ON THE PORE STRUCTURE OF RICE HUSK-DERIVED ACTIVATED CARBON
Main Article Content
Abstract
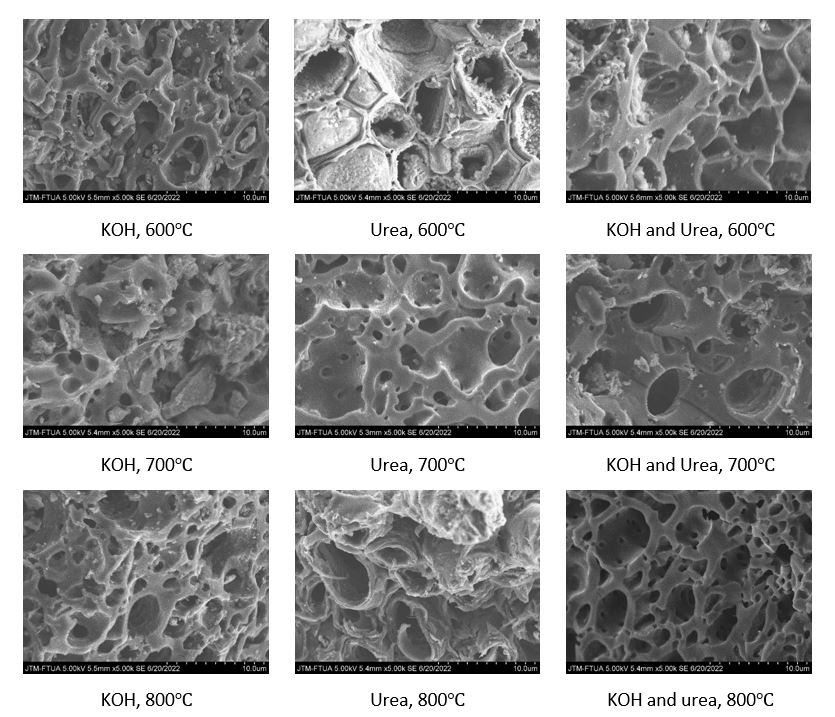
This study investigates the optimization of production parameters for rice husk-derived activated carbon, aiming for its effective application in direct air capture (DAC) technology. Various chemical activation agents (potassium hydroxide [KOH], urea, and their combination) and activation temperatures (600°C, 700°C, and 800°C) were explored using pyrolysis. The resulting activated carbon's morphology was analyzed via scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and ImageJ. Results demonstrate that both activation agent choice and temperature significantly influence pore diameter size and quantity. Increased temperatures led to smaller pore diameters and higher pore quantities. The combination of KOH and urea at 800°C produced the most favorable particle size (0.811 μm), suitable for applications requiring a well-defined pore structure. This combination also exhibited the most even pore distribution and highest pore density. These findings provide valuable insights for optimizing the production of rice husk-derived activated carbon, aiding in the development of sustainable and effective sorbents for CO₂ capture in DAC technology. Additionally, they offer potential for broader applications of husk-activated carbon in various industrial and environmental fields.
Downloads
Article Details
Transfer of Copyrights
- In the event of publication of the manuscript entitled [INSERT MANUSCRIPT TITLE AND REF NO.] in the Malaysian Journal of Science, I hereby transfer copyrights of the manuscript title, abstract and contents to the Malaysian Journal of Science and the Faculty of Science, University of Malaya (as the publisher) for the full legal term of copyright and any renewals thereof throughout the world in any format, and any media for communication.
Conditions of Publication
- I hereby state that this manuscript to be published is an original work, unpublished in any form prior and I have obtained the necessary permission for the reproduction (or am the owner) of any images, illustrations, tables, charts, figures, maps, photographs and other visual materials of whom the copyrights is owned by a third party.
- This manuscript contains no statements that are contradictory to the relevant local and international laws or that infringes on the rights of others.
- I agree to indemnify the Malaysian Journal of Science and the Faculty of Science, University of Malaya (as the publisher) in the event of any claims that arise in regards to the above conditions and assume full liability on the published manuscript.
Reviewer’s Responsibilities
- Reviewers must treat the manuscripts received for reviewing process as confidential. It must not be shown or discussed with others without the authorization from the editor of MJS.
- Reviewers assigned must not have conflicts of interest with respect to the original work, the authors of the article or the research funding.
- Reviewers should judge or evaluate the manuscripts objective as possible. The feedback from the reviewers should be express clearly with supporting arguments.
- If the assigned reviewer considers themselves not able to complete the review of the manuscript, they must communicate with the editor, so that the manuscript could be sent to another suitable reviewer.
Copyright: Rights of the Author(s)
- Effective 2007, it will become the policy of the Malaysian Journal of Science (published by the Faculty of Science, University of Malaya) to obtain copyrights of all manuscripts published. This is to facilitate:
- Protection against copyright infringement of the manuscript through copyright breaches or piracy.
- Timely handling of reproduction requests from authorized third parties that are addressed directly to the Faculty of Science, University of Malaya.
- As the author, you may publish the fore-mentioned manuscript, whole or any part thereof, provided acknowledgement regarding copyright notice and reference to first publication in the Malaysian Journal of Science and Faculty of Science, University of Malaya (as the publishers) are given. You may produce copies of your manuscript, whole or any part thereof, for teaching purposes or to be provided, on individual basis, to fellow researchers.
- You may include the fore-mentioned manuscript, whole or any part thereof, electronically on a secure network at your affiliated institution, provided acknowledgement regarding copyright notice and reference to first publication in the Malaysian Journal of Science and Faculty of Science, University of Malaya (as the publishers) are given.
- You may include the fore-mentioned manuscript, whole or any part thereof, on the World Wide Web, provided acknowledgement regarding copyright notice and reference to first publication in the Malaysian Journal of Science and Faculty of Science, University of Malaya (as the publishers) are given.
- In the event that your manuscript, whole or any part thereof, has been requested to be reproduced, for any purpose or in any form approved by the Malaysian Journal of Science and Faculty of Science, University of Malaya (as the publishers), you will be informed. It is requested that any changes to your contact details (especially e-mail addresses) are made known.
Copyright: Role and responsibility of the Author(s)
- In the event of the manuscript to be published in the Malaysian Journal of Science contains materials copyrighted to others prior, it is the responsibility of current author(s) to obtain written permission from the copyright owner or owners.
- This written permission should be submitted with the proof-copy of the manuscript to be published in the Malaysian Journal of Science
Licensing Policy
Malaysian Journal of Science is an open-access journal that follows the Creative Commons Attribution-Non-commercial 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC 4.0)
CC BY – NC 4.0: Under this licence, the reusers to distribute, remix, alter, and build upon the content in any media or format for non-commercial purposes only, as long as proper acknowledgement is given to the authors of the original work. Please take the time to read the whole licence agreement (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode ).
References
Cannone, S. F., Lanzini, A., & Santarelli, M. (2021). A review on CO2 capture technologies with focus on CO2-enhanced methane recovery from hydrates. In Energies (Vol. 14, Issue 2). MDPI AG. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14020387
Deng, Y., Li, J., Miao, Y., & Izikowitz, D. (2021). A comparative review of performance of nanomaterials for Direct Air Capture. Energy Reports, 7, 3506–3516. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egyr.2021.06.002
Dissanayake, P. D., You, S., Igalavithana, A. D., Xia, Y., Bhatnagar, A., Gupta, S., Kua, H. W., Kim, S., Kwon, J. H., Tsang, D. C. W., & Ok, Y. S. (2020). Biochar-based adsorbents for carbon dioxide capture: A critical review. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 119(November 2019), 109582. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2019.109582
Elhenawy, S. E. M., Khraisheh, M., Almomani, F., & Walker, G. (2020). Metal-organic frameworks as a platform for CO2 capture and chemical processes: Adsorption, membrane separation, catalytic-conversion, and electrochemical reduction of CO2. Catalysts, 10(11), 1–33. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10111293
Goembira, F., Aristi, D. M., Nofriadi, D., & Putri, N. T. (2021). Analisis Konsentrasi PM2,5, CO, dan CO2, serta Laju Konsumsi Bahan Bakar Biopelet Sekam Padi dan Jerami pada Kompor Biomassa. Jurnal Ilmu Lingkungan, 19(2), 201–210. https://doi.org/10.14710/jil.19.2.201-210
Hussin, F., Aroua, M. K., Yusoff, R., & Szlachta, M. (2021). Preparation of eco-friendly adsorbent for enhancing CO2 adsorption capacity. Separation Science and Technology (Philadelphia), 00(00), 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1080/01496395.2021.1998122
Jouhara, H., Ahmad, D., van den Boogaert, I., Katsou, E., Simons, S., & Spencer, N. (2018). Pyrolysis of domestic based feedstock at temperatures up to 300 °C. Thermal Science and Engineering Progress, 5(October 2017), 117–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsep.2017.11.007
Lee, J. W., Kim, S., Torres Pineda, I., & Kang, Y. T. (2021). Review of nanoabsorbents for capture enhancement of CO2 and its industrial applications with design criteria. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 138(March 2020), 110524. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2020.110524
Lushpa, N. V, Lawah, A. I., Chernyakova, K. V., & Vrublevs, I. A. (2018). Using The ImageJ Software for Determining Parameters Of Microstructure Of Nanoporous Materials By The Results Of SEM Image Processing. Big Data and Advanced Analytics, 3–4.
Rinawati, Hidayat, D., Supriyanto, R., Permana, D. F., & Yunita. (2019). Adsorption of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons using Low-Cost Activated Carbon Derived from Rice Husk. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 1338(1). https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1338/1/012005
Segneri, V., Trinca, A., Libardi, N., Colelli, L., Micciancio, M., & Vilardi, G. (2023). Nanoparticles used for CO2 Capture by Adsorption: a Review. Chemical Engineering Transactions, 101, 133–138. https://doi.org/10.3303/CET23101023
Shi, X., Xiao, H., Azarabadi, H., Song, J., Wu, X., Chen, X., & Lackner, K. S. (2020). Sorbents for the Direct Capture of CO2 from Ambient Air. In Angewandte Chemie - International Edition (Vol. 59, Issue 18, pp. 6984–7006). Wiley-VCH Verlag. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201906756
Wang, X., Chen, Y., Xu, W., Lindbråthen, A., Cheng, X., Chen, X., Zhu, L., & Deng, L. (2023). Development of high capacity moisture-swing DAC sorbent for direct air capture of CO2. Separation and Purification Technology, 324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2023.124489
Yaumi, A. L., Bakar, M. Z. A., & Hameed, B. H. (2018). Melamine-nitrogenated mesoporous activated carbon derived from rice husk for carbon dioxide adsorption in fixed-bed. Energy, 155, 46–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2018.04.183
Zhang, X., Huang, Y., Gao, H., Luo, X., Liang, Z., & Tontiwachwuthikul, P. (2019). Zeolite catalyst-aided tri-solvent blend amine regeneration: An alternative pathway to reduce the energy consumption in amine-based CO2 capture process. Applied Energy, 240(February), 827–841. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2019.02.089